Be it Amazon purchase, Instagram feed or Netflix suggestions, almost every interaction with technology involves DATA. Let’s discuss the prime example of one of the top e-shopping sites #Amazon. Ever wondered what enables Amazon to tailor its homepage displays to your preferences? Suppose, if you search for a study table or bookshelf, Amazon will not display product recommendations for monsoon wear. Instead, what you’ll see is a chair, stationary material or desk organizer, which many of us may get tempted to purchase.
How is this possible?
Yes! You are right! With the help of available data and data science.
If you recall your shopping experience with Amazon, you would easily get how useful data collecting can be to the customer and the company. The data set recalls what you’ve purchased, how much you have spent and which items you have browsed in the time you spent on the site.
What is Data Science?
The availability of data and the need for data science skills and data-driven decision making have skyrocketed over the last decade. Data science skills are vital across industries and the data scientist job is undoubtedly the trendiest career option.
You are probably thinking to yourself right now, “Okay, all this sounds interesting!. “How do I get into data science?” And you are certainly not alone. Big data is surrounded by a lot of hype. Organizations and individuals are always leaving digital footprints when they browse, all the time, and everywhere. And someone has to deal with that information. In simpler terms, data scientists build up the systems needed to derive insights from massive amounts of data. With data being gathered in many parts of life, from marketing to healthcare, and even sports, resource management, entertainment, being able to extract meaningful information from data is a very powerful position to be in.
In a nutshell, the field of Data science includes developing ways to store, report, and analyse data to extract useful information for making informed decisions.
Applications are numerous and so are the opportunities. It wouldn’t be wrong to say this is just the beginning.
While having alternatives is usually a good thing, it may be tough to comprehend how different jobs differ and what kind of skill sets and educational backgrounds are necessary for each. This can be difficult for people who are just starting out in the field of data science.
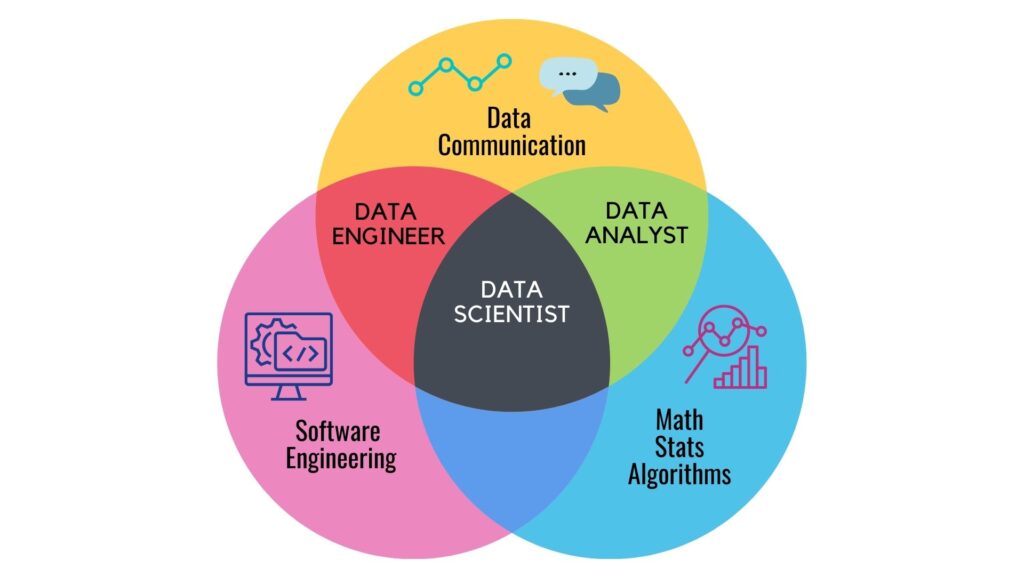
Data Scientists vs. Data Analysts vs Data Engineer: What’s the Difference?
Entry-level data science positions and data analysts frequently overlap in terms of skills and work duties. The three professions described below have responsibilities that need statistical knowledge as well as programming skills. However, there is a clear difference among all the three.
Data Scientist: Data scientists use data to answer questions about the company. They use data to develop new product features. They will spend a significant amount of time cleaning data to ensure that it is suitable for their models and machine learning techniques. Machine learning algorithms and data science are at work when you watch Netflix and get a customised list of recommended shows.
Data Analyst: Data related queries are addressed by Data analysts. Data analysts, unlike data scientists, are not concerned with utilising data to identify patterns or predict the future of an organisation. Their responsibilities include analysing historical data, designing systems for storing data and utilising various tools for analysing data.
Data Engineer: Data engineers are tasked with developing, constructing, and managing data systems. They ensure that the available data is ready for processing and analysis in a format that can be easily analysed.
Where do data scientists work?
Now is the time to start creating professional networks by making contacts within student communities. Look for internship possibilities, and seek advice from instructors and advisers.
Companies are keen to fill entry-level data science positions. Look for jobs like Junior Data Analyst or Junior Data Scientist. Data science, maybe more than any other, is a job on the rise, having been regularly ranked as one of the most in-demand industries for much of the last decade.
Data scientists can work in various sectors. Those might include:
- Government
- Research and development
- Computer systems design
- Colleges and universities
- Software companies
- Automobile industries
- Delivery companies
- Tech companies
Moving ahead, we will discuss the qualities and skills a candidate for these roles needs to possess and how to become a data scientist.
How to become a data scientist?
Future data scientists can begin today even before enrolling in an online degree programme. Acquiring proficiency in the most frequently used programming languages in data science (such as Python, Java, and R) as well as brushing up on applied math and statistics can give aspiring data scientists a leg up. In reality, attending college with a pre-existing skill set often boosts students’ learning rate.
Most importantly, early exposure to data science knowledge needs might help you decide whether a data science job is indeed a good fit for you.
What educational qualifications do I need?
Majors in data science include statistics, computer science, information technology, mathematics, or data science. If you’re already enrolled in another undergraduate programme, then at least minoring in one of the disciplines would be of great help.
Here are things to add to your “to-do” list:
- Discover the fundamentals of applied mathematics
- Understand the fundamentals of programming (mainly Python)
- Acquire a fundamental understanding of database languages
- Enrol in a job-ready course. Perform a Data Science Project
What are the ‘must-have’ skills?
Data scientists, like many of the professions listed, must have analytic, machine learning, and statistical abilities, as well as knowledge of algorithms and coding. However, one of the most crucial qualities a competent data scientist possesses is the ability to explain the meaning of data in a way that others can understand. Excellent verbal and written communication skills are essential for this profession.

- Technical skills – Math (calculus, and probability and linear algebra), Statistics, machine learning tools and techniques, data visualisation and reporting techniques and a few more. Experience with many of these computer programs: SAS, SPSS, MATLAB R, Java, Python, C/C++, SQL/NoSQL Databases.
- Communication skills – A data scientist is capable of clearly communicating technical and analytical conclusions to a non-technical department. In order to properly analyse the data, they must also be able to fully understand the demands of their non-technical departments (such as business development or marketing teams). A data scientist must enable corporate decision-making by delivering reliable information.
So far, we have discussed different aspects of data-driven career paths. With so many alternatives available, how does one get started in this field?
We heard you!
We have curated a bunch of the best resources to kick-start your data science journey. Head on to each individual resource for more comprehensive information which may help you make an informed choice.
| Beginner’s Guide | Read | Explore |
| Learn | Participate and Network |
